Benzene Definition
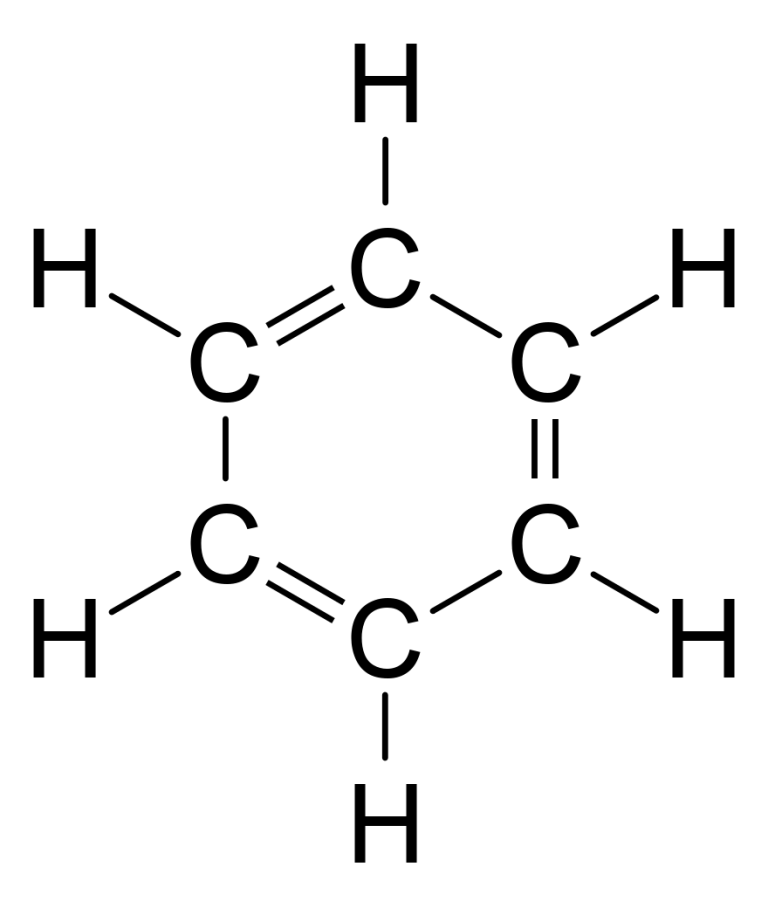
Benzene (C6H6), simplest organic, aromatic hydrocarbon and parent compound of numerous important aromatic compounds. Benzene is a colourless liquid with a characteristic odour and is primarily used in the production of polystyrene. It is highly toxic and is a known carcinogen; exposure to it may cause leukemia. As a result, there are strict controls on benzene emissions.(More) Benzene was first discovered by the English scientist Michael Faraday in 1825 in illuminating gas. In 1834 German chemist Eilhardt Mitscherlich heated benzoic acid with lime and produced benzene. In 1845 German chemist A.W. von Hofmann isolated benzene from coal tar.
Benzene Applications
- Used in preparation of phenol.
- Used in preparation of aniline (for dyes).
- Used in preparation of dodecylbenzene (for detergents).
- Used in the manufacture of nylon fibers.
- Used to make some types of rubbers, lubricants, dyes, detergents, drugs, explosives, and pesticides.
- Used as a constituent in motor fuels.
- Used as a solvent for fats, waxes, resins, oils, inks, paints, plastics, and rubber.
- Used as a chemical intermediate.
- Adhesives and sealants.
- Automotive care products.
- Chemical Feed Stock.
- Cleaning and furnishing care products.
- Food packaging.
- Fuels and related products.
- Intermediate.
- Intermediates.
- Lubricants and greases.
- Metal products not covered elsewhere.
- Not known or reasonably ascertainable.
- Paper products.
- Plastic and rubber products not covered elsewhere.
- Sold to re-sellers for petroleum fuel and petrochemical industry.
- Petrochemicals.
CHARACTERISTICS
- Toxic.
- Volatile.
- Flammable.
- Liquid hydrocarbon.
- Clear.
- Colorless.
- Gasoline-like odor.
- Boiling Point : 80°C
- Melting Point : 6°C
- Flash Point : -11°C c.c.
- Miscible with alcohol, chloroform, ether, carbon disulfide, acetone, oils, carbon tetrachloride, and glacial acetic acid.
| CHARACTERISTIC | Value |
| Molecular Weight | 78.114 g/mol |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 0 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Complexity | 15.5 |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 0 A^2 |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 78.047 g/mol |
| Exact Mass | 78.047 g/mol |
| XLogP3 | 2.1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | true |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 6 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
